
Everything You Need To Know About Oxalate Dumping Ripples of Life
Characterized by symptoms like fatigue, dizziness, pain, and irritability, oxalate dumping is said to occur when you decrease your intake of oxalates too quickly. Fortunately, several.

What Is Oxalate Dumping? The Kidney Dietitian
Common symptoms of oxalate dumping include: Increased urinary frequency and urgency Cloudy or foul-smelling urine Abdominal pain or discomfort Joint pain and stiffness Headaches and migraines.

Oxalate Dumping Symptoms What to Expect Low oxalate recipes, Low oxalate, Symptoms
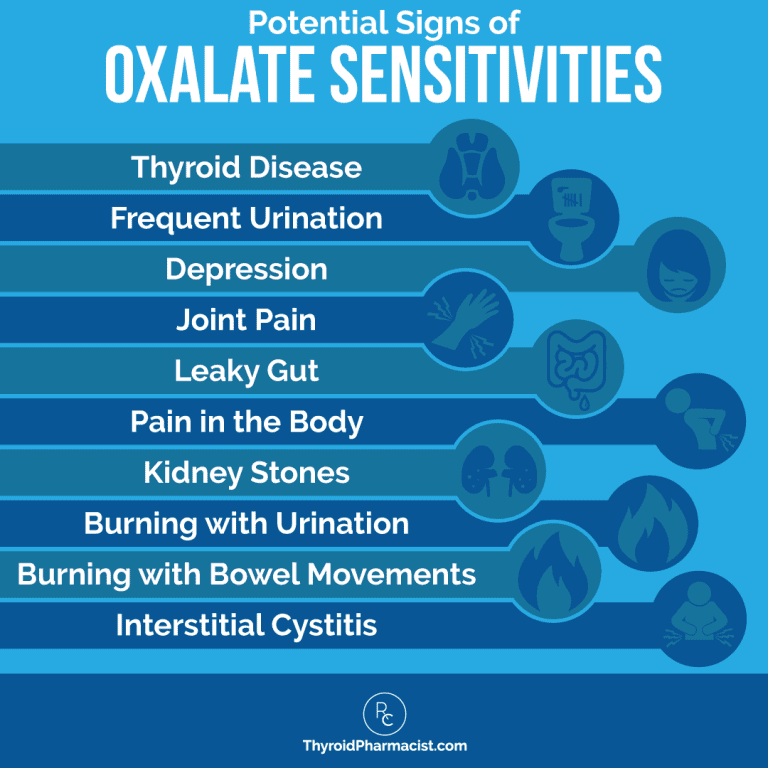
In addition to thyroid symptoms, are you also experiencing joint pain, burning with urination, burning with bowel movements — and/or do you have a history of kidney stones? If so, you may want to look into oxalate sensitivity. Oxalates are found in certain "healthy" foods such as dark leafy vegetables and legumes, as well as some nuts and seeds.

Oxalates, Salicylates, and Histamine Intolerance What's the Connection? Dr Becky Campbell
Oxalate dumping can result in a range of symptoms, including joint pain, kidney stones, and digestive issues. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for oxalate dumping, as well as provide some tips on how to manage this condition effectively. Table of Contents What are Oxalates

Everything You Need To Know About Oxalate Dumping Ripples of Life
You might have heard oxalate dumping comes along with symptoms like dizziness, fatigue, pain, and irritability, and you definitely don't want that! So, what's the deal with oxalate dumping? Let's delve into the details of oxalates and oxalate dumping. What are Oxalates?
What Are Oxalate Dumping Symptoms? The Healthy Consultant
Symptoms of oxalate dumping could be pain experienced during urinating or defecating, grainy stools, yeast flare, and associated irritability. It is seen that Individuals on the autism spectrum disorder have elevated levels of oxalates as compared to neurotypical individuals. This becomes extremely difficult to diagnose as these kids are not.
Oxalates on a Gluten Free Diet Friend or Foe? Gluten Free Society
Often, a person with oxalate issues will experience some temporary worsening of several symptoms after being on a truly low oxalate diet for a while. This could be a sign that cells are moving stored oxalate out and being damaged in the process. Sticking with the diet is an important part of waiting out the healing process.

Oxalate Poisoning & Dumping What It Looks Like, the Microbiome Myth & Why Zero Carb May Not
Having a diet high in oxalates has been shown to increase the oxalate levels in urine and the general scientific consensus is that higher urinary oxalate levels increase the risk of developing kidney stones, or nephrolithiasis, in susceptible individuals.

How to Avoid Oxalate Toxicity & Avoid Oxalate Dumping Food sensitivities, Nutrigenomics
Mayo Clinic Overview Hyperoxaluria (hi-pur-ok-suh-LU-ree-uh) happens when you have too much oxalate in your urine. Oxalate is a natural chemical the body makes. It's also found in some foods. But too much oxalate in the urine can cause serious problems.

12 High Oxalate Foods and How They Cause Damage
What Is Oxalate? First, what is oxalate itself? Oxalate is a "non-nutrient" that is found in many healthy plant foods such as spinach, almonds, raspberries, and potatoes. Plants make oxalate as way to regulate calcium and for protection. ( 1) However, as far as we know, oxalate does not have a function for us humans. Oxalate & Kidney Health
How Oxalates Affect Thyroid Health Dr. Izabella Wentz, PharmD
It takes about 3/4 cup raw broccoli (about 6.5 mg. oxalate) to steam down to 1/2 cup steamed broccoli (about 6.5 mg. oxalate) or to boil down to about 1/2 cup boiled broccoli (about 1.1 mg. oxalate). You'll notice that steaming and roasting usually don't decrease oxalate, while boiling often does.

Health Dangers of Oxalates Kevin Stock
In additional to oxalates that originate in food, called exogenous oxalates, the human body also produces them mainly in the liver from excess vitamin C, fructose, and yeast. (Other anti-nutrients include phytic acid and lectins). Unfortunately, oxalates form painful crystals in various places such as the kidneys, bladder, vulva, gut wall, and.

Could oxalate toxicity be the cause of your symptoms?
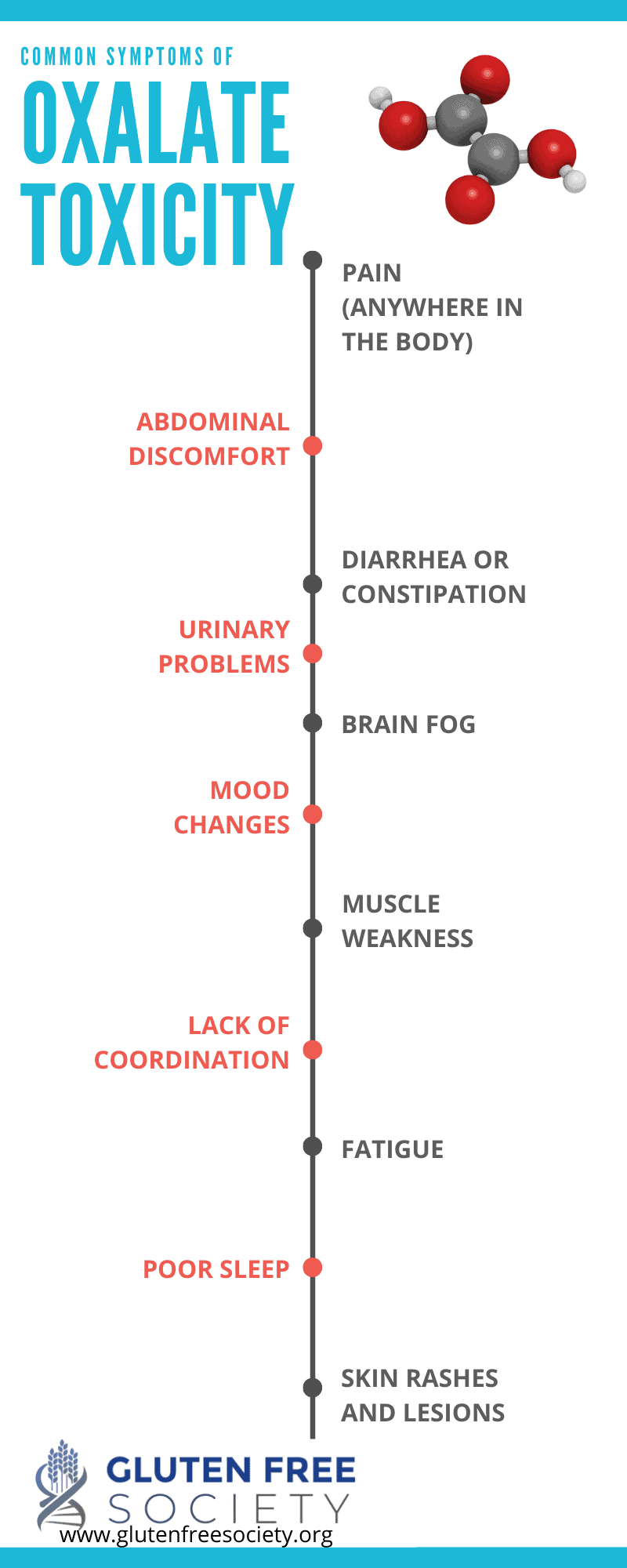
Symptoms of Oxalate Dumping Symptoms vary from person to person, but may include: Skin: Rashes, tiny white acne-like pustules, or small oxalate crystals actually being pushed to the surface of the skin Urinary: Cloudy urine, bladder and/or kidney tenderness, UTI-like symptoms Stool: Burning bowel movements, as if you ate something spicy

DETOX // detoxing symptoms to watch out for! (all about oxalate dumping and the "keto flu
The liver is an organ that converts everything you eat or drink into nutrients and gets rid of toxins. With primary hyperoxaluria, your liver does not make enough of a certain protein to prevent oxalate (a natural chemical in your body) from building up in your body. Oxalate builds up in the kidneys and causes kidney stones and kidney damage.

How to identify Oxalates as a health issue and prevent Oxalate Dumping symptoms. YouTube
The symptoms of oxalate dumping typically go away in a couple of days, up to several weeks. Since a build-up of oxalates may result in chronic inflammation , some believe those with an inflammatory-related condition like Crohn's disease or rheumatoid arthritis may benefit from oxalate dumping.

What Is Oxalate Dumping? The Kidney Dietitian
Painful eyes or sandy eyes Brain fog Fatigue Gum issues Interstitial Cystitis Depression Migraines Skin sores and rashes IBS and digestive issues Most people know oxalates collect in the kidneys like oxalate stones but these oxalates can collect all over the body mimicking things like arthritis.